Sustainability
Home >> Sustainability
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Sustainability
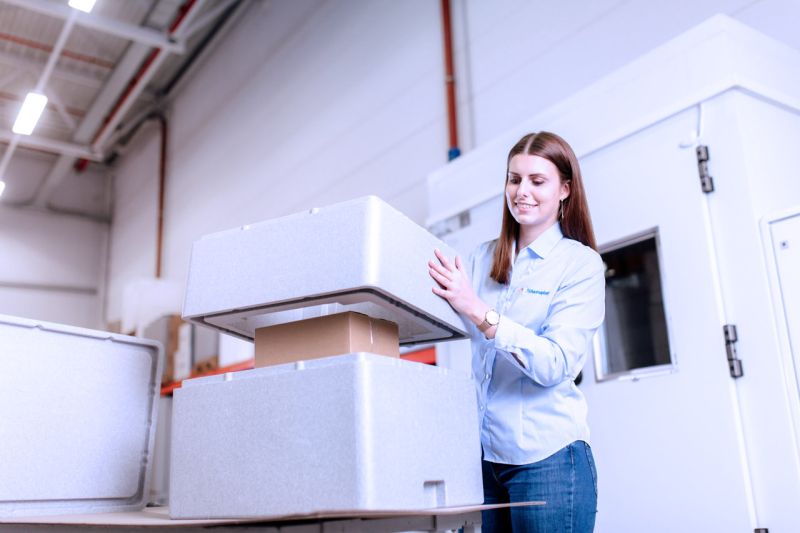
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a standout choice for sustainability, thanks to its ability to be recycled, save energy, and use resources wisely. Despite what some people might think, EPS is good for the planet. It’s made with care to reduce its impact on global warming and is even made from recycled materials. EPS is used in many ways, from keeping products safe during shipping to making buildings more energy-efficient.
The process of making EPS is smart and eco-friendly. It uses less energy and water, and any leftover pieces from making EPS products are recycled back into new ones, leaving no waste behind. Plus, new technology in making EPS means even less energy is used, which is better for the environment.
EPS is also incredibly lightweight, which means it costs less to transport goods, reducing fuel use and pollution. Its excellent insulation properties keep products at the right temperature, lowering the chance of damage. In construction, EPS helps build things faster and makes buildings last longer without losing heat or cool air.
Overall, choosing EPS is a smart move for the environment. It’s all about using less and recycling more, making it a key player in a future where we take better care of our planet.

EPS: The Facts
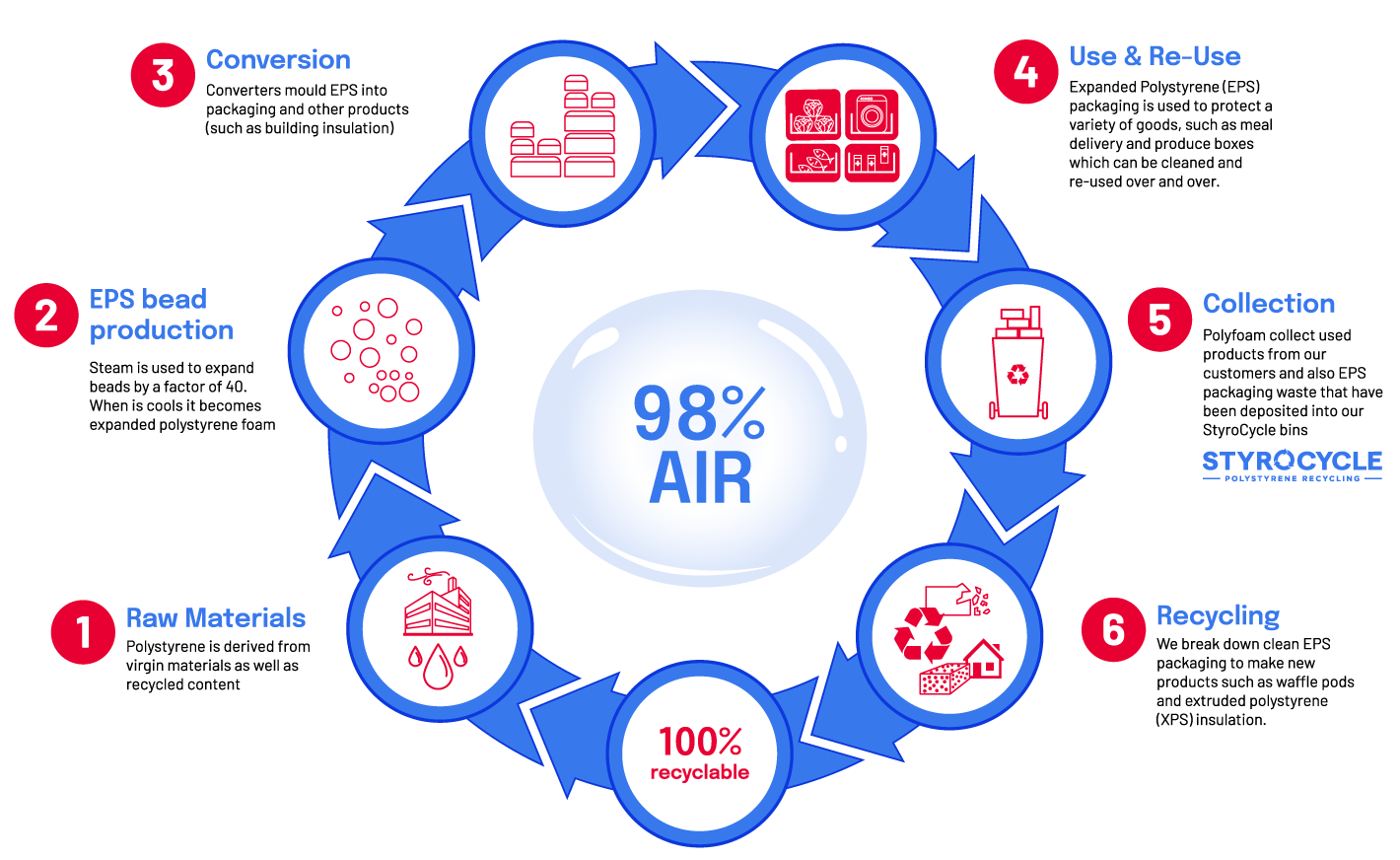
 Expanded polystyrene (EPS) consists of 98% air, and only 2% plastic. This makes EPS an exceptionally efficient packaging material in terms of resource use and its minimal carbon footprint.
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) consists of 98% air, and only 2% plastic. This makes EPS an exceptionally efficient packaging material in terms of resource use and its minimal carbon footprint. The ultra-light nature of EPS contributes to lower fuel usage during the transportation of goods, compared to heavier packaging alternatives.
The ultra-light nature of EPS contributes to lower fuel usage during the transportation of goods, compared to heavier packaging alternatives. EPS's excellent cushioning properties minimise losses from breakage or damage within the supply chain, conserving energy, materials, and transportation resources.
EPS's excellent cushioning properties minimise losses from breakage or damage within the supply chain, conserving energy, materials, and transportation resources. Being a single polymer, expanded polystyrene (EPS) can be easily recycled into products that save energy, like insulation or void-fill for eco-friendly construction.
Being a single polymer, expanded polystyrene (EPS) can be easily recycled into products that save energy, like insulation or void-fill for eco-friendly construction. EPS does not contain HFCs, CFCs, or HCFCs, and utilizes Pentane as a blowing agent, which has a low Global Warming Potential (GWP) of under five.
EPS does not contain HFCs, CFCs, or HCFCs, and utilizes Pentane as a blowing agent, which has a low Global Warming Potential (GWP) of under five. Styrene, which is used to produce EPS, is naturally found in everyday foods such as strawberries, beans, nuts, beer, wine, coffee beans, and cinnamon.
Styrene, which is used to produce EPS, is naturally found in everyday foods such as strawberries, beans, nuts, beer, wine, coffee beans, and cinnamon. EPS is inert and harmless, it does not break down to release chemicals into water or air, thus avoiding contributions to global warming.
EPS is inert and harmless, it does not break down to release chemicals into water or air, thus avoiding contributions to global warming. The manufacturing of expanded polystyrene (EPS) is an environmentally low-impact process using steam as a primary resource, with water recycled multiple times and zero waste, as all excess material is re-purposed.
The manufacturing of expanded polystyrene (EPS) is an environmentally low-impact process using steam as a primary resource, with water recycled multiple times and zero waste, as all excess material is re-purposed. Manufacturing EPS requires only 0.1% of the total global oil consumption.
Manufacturing EPS requires only 0.1% of the total global oil consumption.Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Life Cycle
What is EPS and Why Is It Sustainable?
Explore the importance of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) in our lives and its environmental impact in this informative video by Expanded Polystyrene Australia (EPSA). Learn about the role of expanded polystyrene, also known as styrofoam, in packaging and insulation, and how it’s 100% recyclable, designed for a circular economy. This video highlights the sustainability of EPS, made of 98% air, and its applications from protecting electronics to food transportation.


